匡星星副教授课题组发表两篇高水平论文,报道其在地下水领域的最新研究进展
近日,匡星星副教授课题组与香港大学焦赳赳教授课题组在水资源领域高水平期刊Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 和Hydrological Processes发表2篇论文,报道其在青藏高原地下水研究中取得的最新进展。
第一篇论文题为“Evaluation of lacustrine groundwater discharge, hydrologic partitioning, and nutrient budgets in a proglacial lake in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: using 222Rn and stable isotopes”,通过对典型冰前湖希门错的高分辨氡-222同位素的连续监测建立forward inverse modeling对希门错的湖相地下水排泄进行了高分辨的量化,并耦合稳定氢氧同位素组分build-up模型,对冰前湖的水循环进行了分配。结论显示地下水输入占湖水总输入的~7%。进一步结合地下水端元碳-氮-磷等营养盐组分进行分析,得出地下水为冰前湖的主要无机氮源之一。本研究首次在青藏高原开展基于氡-222同位素量化地下水输入和水循环配比,对高海拔冰前湖地下水输入、水循环及其营养循环具有很好的指示作用。
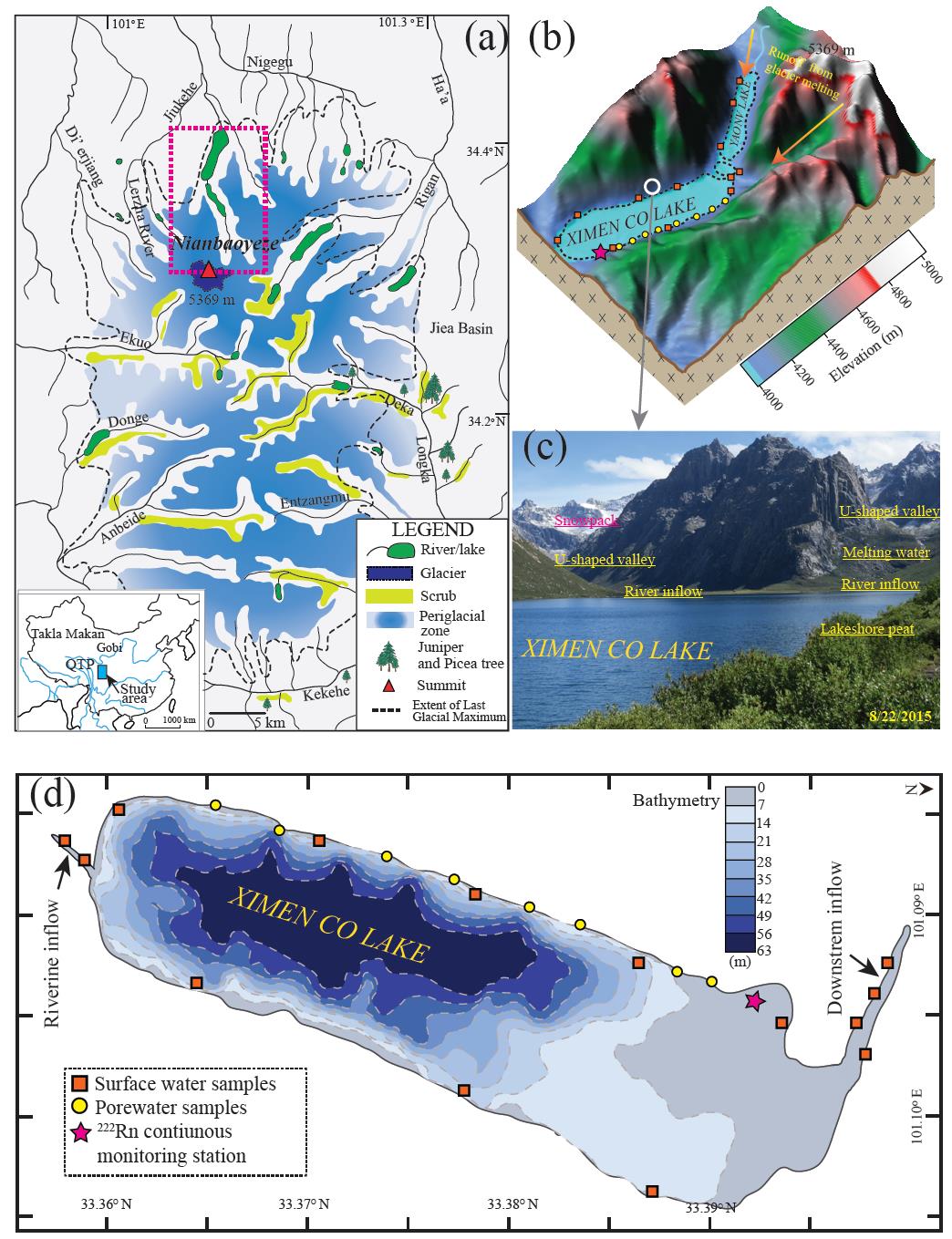
研究区域和采样设置
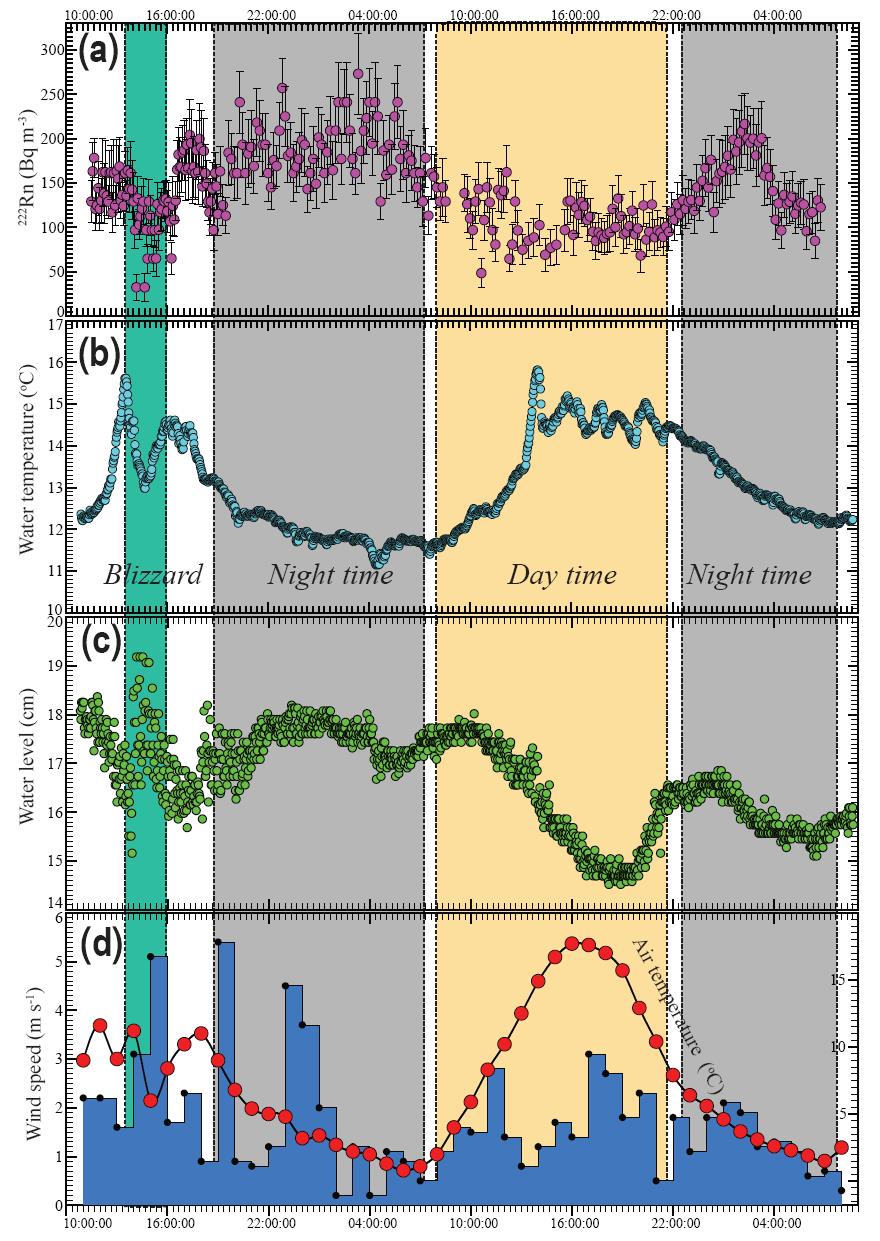
希门错连续观测数据
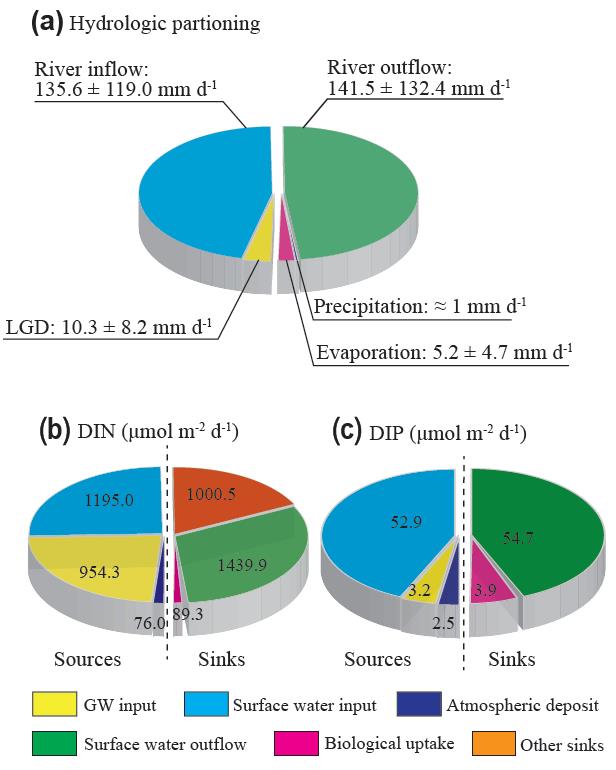
希门错水均衡分析和营养分析
第二篇论文题为“Using stable isotopes of surface water and groundwater to quantify moisture sources across the Yellow River source region”,通过黄河源区不同水体(河水、湖水、地下水)的氢氧同位素特征,识别出该区夏季降水的外部水汽来源为Indian Summer Monsoon和Westerlies的混合,此外,当地水循环(local water recycling)和云下蒸发(subcloud evaporation)也对该区夏季降水起了重要的作用。该研究还建立了一个黄河源区及其周边区域的氢氧同位素的高程模型,该模型可用于黄河源区古高程的重建。

河源区地理位置以及采样点分布
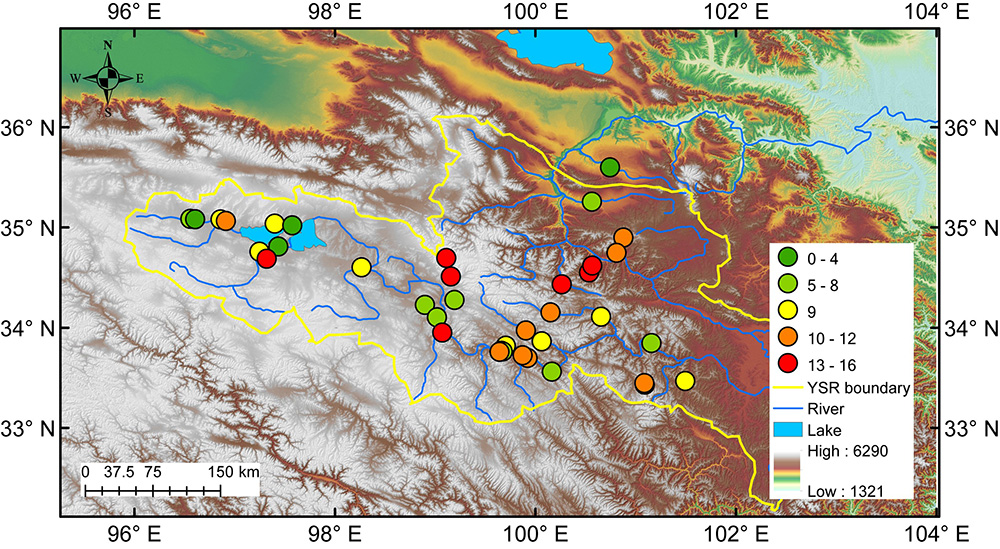
黄河源区支流δ18O的分布
论文信息及链接:
1. Luo, X., X. Kuang, J. J. Jiao*, S. Liang, R. Mao, X. Zhang, and H. Li (2018), Evaluation of lacustrine groundwater discharge, hydrologic partitioning, and nutrient budgets in a proglacial lake in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: using 222Rn and stable isotopes, Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 22(10), 5579–5598.
https://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/22/5579/2018/
2. Kuang, X., X. Luo, J. J. Jiao*, S. Liang, X. Zhang, H. Li, and J. Liu (2019), Using stable isotopes of surface water and groundwater to quantify moisture sources across the Yellow River source region, Hydrological Processes, 1–16, doi:10.1002/hyp.13441.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hyp.13441
以上研究得到了国家自然科学基金(NSFC 41572208、91747204)、香港研究资助局(HKU17304815)以及广东省土壤与地下水污染防控及修复重点实验室等的支持。






